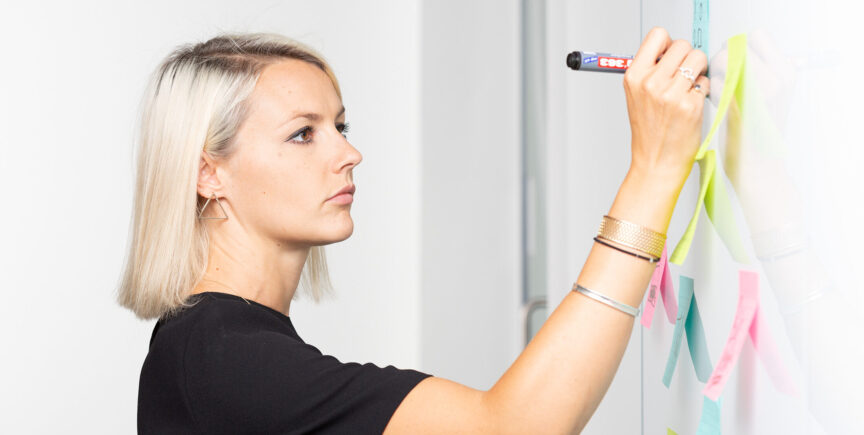
One question which ties up too much time, energy and headspace for most businesses is, “How much should we be paying for photography?”
In the modern business landscape, we have to extend that to videography too, of course. While this article focuses mainly on stills, read to the end for my thoughts on video as well.
The shortest answer I can give is that the corporate communications photography you commission shouldn’t cost you anything. “What?! Free photography?! Where can I get some of that!!” I hear you wail, but of course that notion is ridiculous. Free stuff, as we all know, is often worth exactly what we’ve paid for it.
What I mean is, the photography and videography you commission for your business should, either fairly immediately, or over time, generate more income for your business than it cost to get done. If your photography/videography isn’t winning new clients or gaining fresh business, then you need to look at why it’s not working before deciding you’re paying too much. It could be how you’re deploying the work, it could also be that you’re not paying enough to get the quality you need.
A useful exercise is to start from the other end of the process. Ask what it is you want to achieve with your images, then work backwards to find the solution. That is to say, the photographer you choose is more important than what they charge. Ask yourself if the photographer’s style fits your brand and whether their quality adds a perception of high value to that brand. What they charge should reflect the outcome you’re aiming for. It needs to reflect the quality of their work, the uses to which that work will be put (the Licence to Use) as well as the standard of service they offer.
Just to explain the Licence to Use a little more deeply, a set of photos destined for a one-off press release for a small business won’t command the same fees as a high-production single image used in a national advertising campaign for a global brand.
There are many scenarios between these usage examples, but if you’re open with the photographer about who and what they’re shooting for, they can give far better guidance on the likely fees. And when it comes to the shoot itself, they can plan their own approach and deploy their resources far more effectively for a more successful outcome.
Oh and on that last point, be VERY wary of any photographer who doesn’t ask how the images are to be used. This should be an alarm-bell-moment. If they don’t care what you do with their work, it means they don’t care about your goals. This will be reflected in the results and that’s when photography becomes really expensive, regardless of how cheap it was to acquire.
Much the same approach applies to commissioning video, albeit the costs associated with that tend to focus more on post-production time than on aspects such as licensing. However, if you’re going to commission video, you still need to think carefully about your goals.
Identifying who you’re trying to reach, what their expectations are and how you’re going to win their business should be considered long before commissioning a videographer (ie me!) to press the record button.
If I’m shooting video for a client, of course I want to understand my client’s aims, but I also want to know who they’re trying to win over. If they’re aiming at people who might do business with them, the content, message and production values all need to be of a high quality. There’s no point spending money on a video which is aimless and poor quality. That’s just a waste of money and a drag on valuable resources. It might grab audience attention for a brief moment, but will soon be forgotten in the constant stream of online content marketing. Poor quality production will also harm your brand and cost you sales.
The main message of this post is to think quality first, then work out your budget based on the value you’re likely to gain from the results. Setting out with an unrealistic budget plucked from thin air isn’t going to get you where you need to be, which is why I’m happy to spend time working through these questions with clients before they commit to working with me.
I would be delighted to discuss your stills and video needs, so drop me a line and let’s get your photography and videography making money, not costing it.